Energy Efficiency of External Solar Shades
External solar shades are an effective solution for enhancing the energy efficiency of buildings. These shades, installed on the exterior of windows and facades, play a crucial role in regulating indoor temperatures, reducing the need for artificial cooling, and ultimately lowering energy consumption.
Heat Reduction and Thermal Comfort
One of the primary benefits of external solar shades is their ability to significantly reduce the amount of solar heat entering a building. By blocking direct sunlight, these shades prevent overheating of interior spaces, thus maintaining a more consistent and comfortable indoor temperature. This reduction in heat gain can decrease the reliance on air conditioning systems, leading to substantial energy savings, particularly during hot summer months.
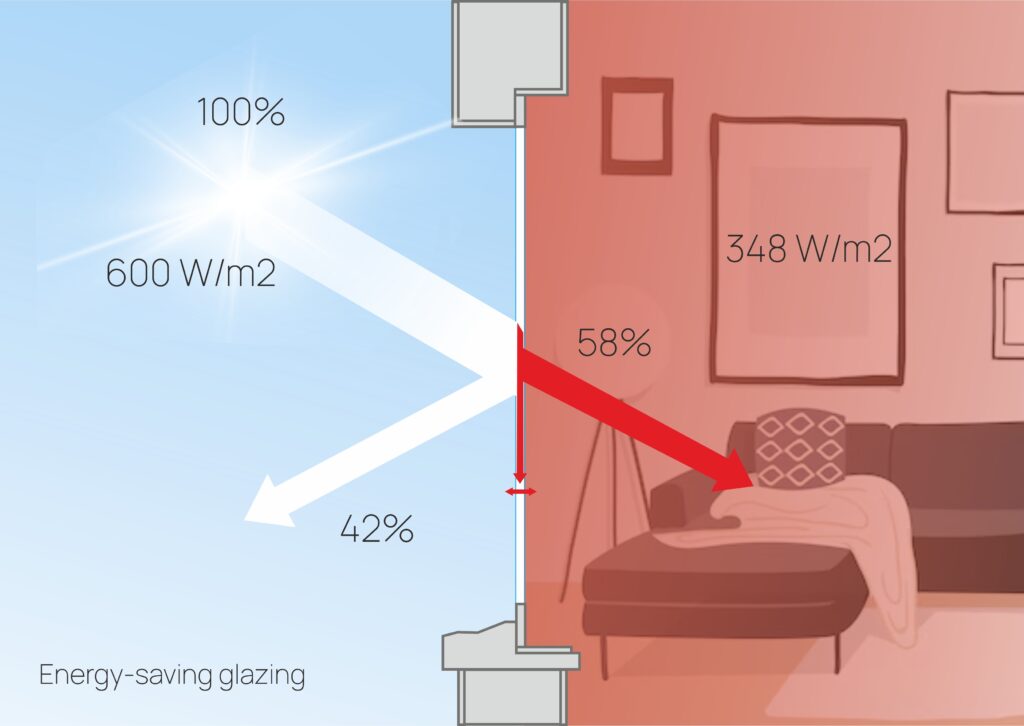
The g coefficient (or solar factor) indicates the amount of solar energy that enters a room through a glass unit. For example, if g = 0.58 (or 58%), and the heat flux is 600 W/m², this means that through 1 square meter of glass, 600 x 0.58 = 348 W of energy will enter the room. Unprotected glass can transmit up to 60% of the solar energy that hits it. Once inside the room, this energy accumulates because the glass is opaque to the long-wave infrared radiation emitted from the heated room.
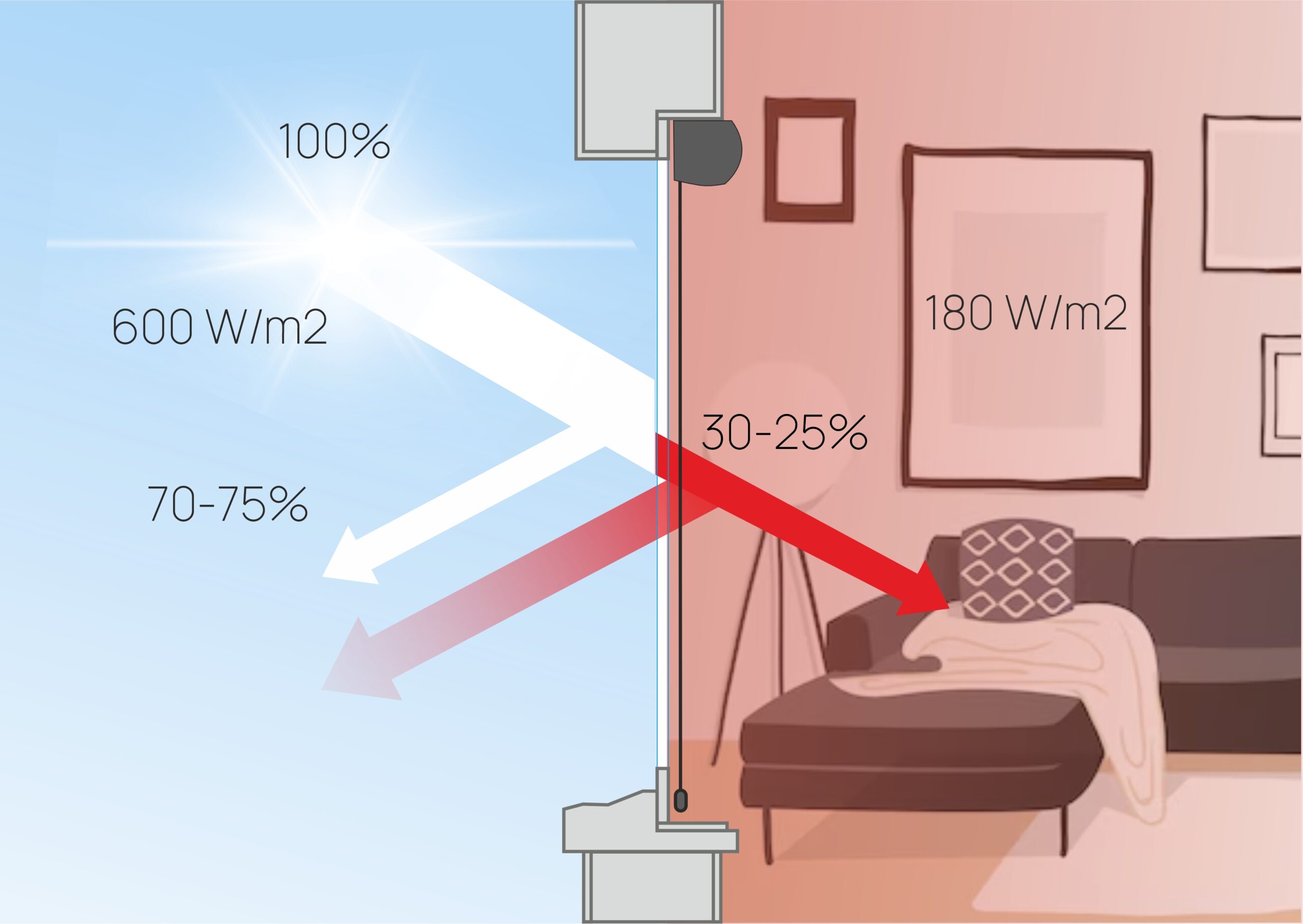
Internal solar protection can reduce the g coefficient to 0.30-0.25. However, for internal solar protection to be effective, materials with high reflectivity must be used, as the energy that enters the room must be reflected back and pass through the glass again. Therefore, on glass with solar control coatings, the effectiveness of internal solar protection is significantly reduced.
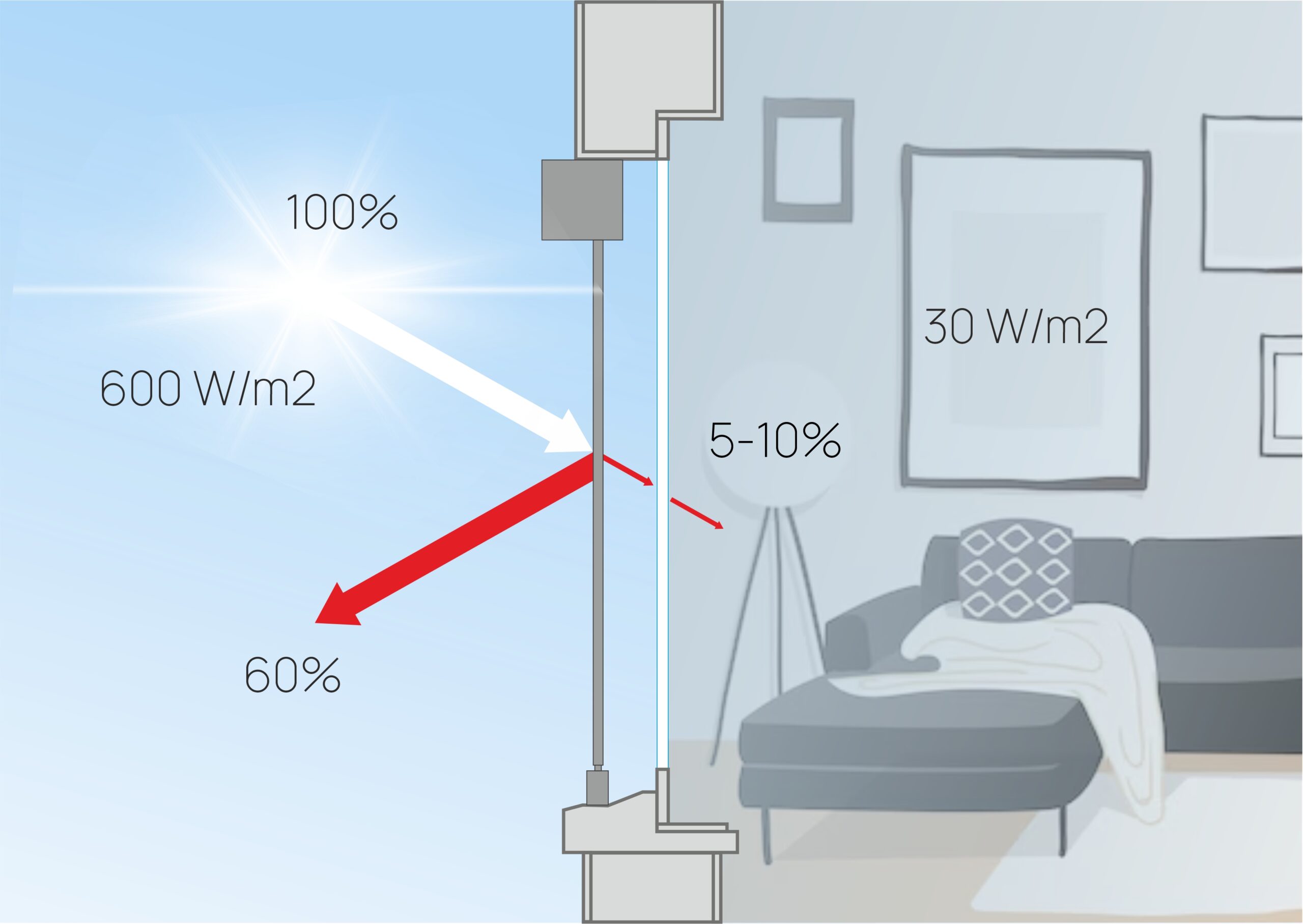
External solar protection is the most effective. Solar energy remains outside, allowing no more than 5-10% to pass into the room. The g coefficient is 0.05 – 0.1. In this case, the solar control properties of the glass have almost no effect on the quality of protection, as all the heat is stopped before it reaches the glass unit. Additionally, we get a dynamic facade and can use solar energy to heat the room during cold weather.
Energy Savings and Cost Reduction
The installation of external solar shades can lead to significant energy savings. By lowering the demand for cooling and lighting, buildings can achieve lower electricity bills and reduced operational costs. In many cases, the initial investment in solar shades is offset by the long-term savings in energy expenses.
Environmental Impact
In addition to cost savings, external solar shades contribute to a reduction in the overall environmental impact of buildings. By decreasing energy consumption, they help lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. This makes external solar shades a sustainable choice for eco-conscious building designs.
Daylighting and Glare Control
External solar shades also contribute to improved daylighting within buildings. By diffusing natural light, they minimize glare while still allowing sufficient daylight to penetrate the interior. This not only enhances occupant comfort but also reduces the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours, further contributing to energy efficiency.
Versatility and Aesthetic Appeal
External solar shades come in various designs, materials, and colors, allowing for customization to match the architectural style of any building. This versatility not only ensures functional benefits but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of the structure. Modern designs can blend seamlessly with the building’s facade, adding a sleek and contemporary look.
External solar shades are a practical and efficient solution for improving the energy performance of buildings. By reducing heat gain, controlling glare, and enhancing natural daylighting, these shades contribute to significant energy savings, cost reduction, and environmental benefits. As a versatile and aesthetically pleasing addition to building exteriors, external solar shades offer a comprehensive approach to achieving greater energy efficiency and sustainability.